Biogas Digester
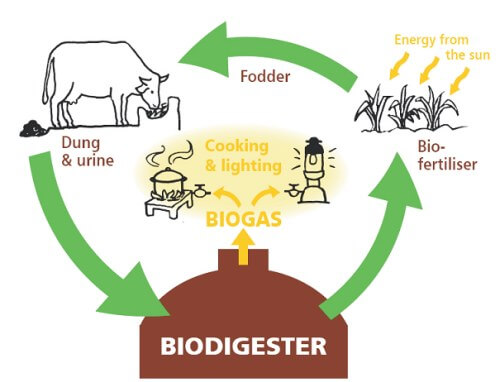
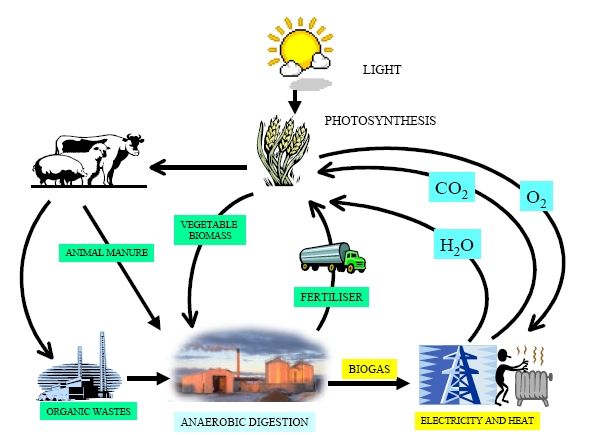
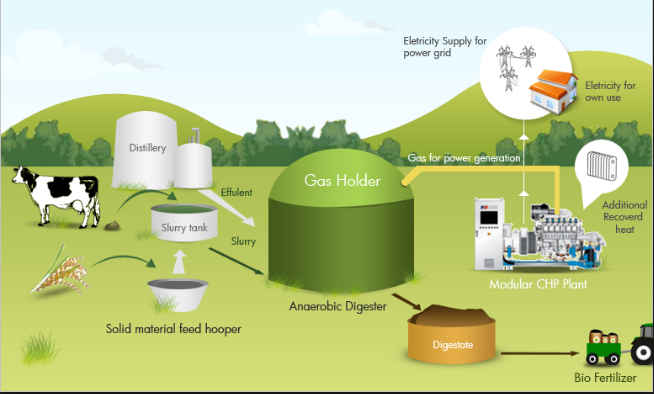
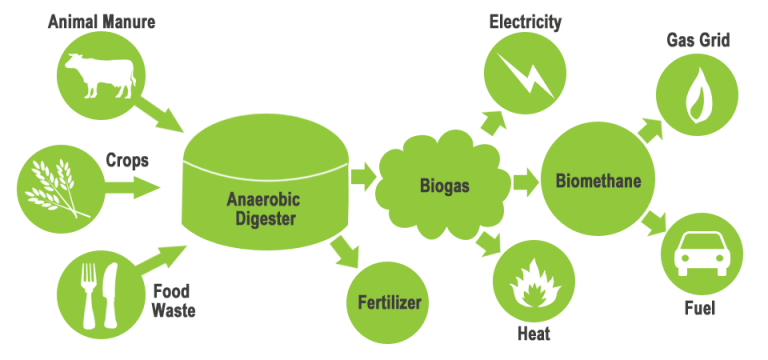
A biogas digester (also known as a biogas plant) is a large tank where inside biogas is produced through the decomposition/breakdown of organic matter through a process called anaerobic digestion. It’s called a digester because organic material is eaten and digested by bacteria to produce biogas. A biogas digester forms the most critical part of biogas production because without it, no biogas would be produced without the breakdown of organic waste or material. To understand how biogas is produced, it’s important to understand the components of a biogas digester, which itself is part of a biogas electric generator plant. A typical biogas digester has a container that holds organic matter and water. This mixture of water and organic matter is called slurry.
Key benefits:
- Collect biogas to be converted into green energy.
- Control odours.
- Provide thermal insulation.
- Lower operating costs.
- Allow access for sampling and maintenance.
- An alternative source of energy.
- Can lower greenhouse gas emissions from sources like manure and food waste.
- Refined to power vehicles that run on natural gas.